“B” is for Bitcoin By William Lama, Ph.D.
“B” is for Bitcoin
By William Lama, Ph.D.
Have you noticed that the kids, and nerds of any age, have their own vocabulary? I remember when men were from Mars and women were from Venus and that fact explained most gender differences. But that was so 20th century. Today the kids and nerds live in the Metaverse, a shared virtual world accessed via the internet.
This digital space is made lifelike via virtual reality or augmented reality. Its domain includes the gaming world, cryptocurrencies and the blockchain. Note the Bitcoin and the chain of blocks in the figure. From the website we learn that “secure Cryptocurrencies with minimal transaction fees will enable on-platform instantly auditable peer to peer transactions.” Also, ownership of digital assets and virtual items in the metaverse will be easy to verify and trade using the underlying secured blockchain.
Note that the kids also change the meaning of words. During the last election cycle, I saw a young girl explain why socialism is great - it’s just shorthand for social media. It’s hard to communicate when your vocabularies don’t match. That is one of the reasons why most people have a difficult time understanding Bitcoin and Blockchain. In my last essay I mentioned a number of new terms that you might explore, including crypto and blockchain and others. You may be surprised to find that a bitcoin wallet does not contain bitcoins and bitcoin mining does not involve a search for bitcoin. Confusing?
Bitcoin Basics
Let’s try to avoid confusion by explaining Bitcoin and Blockchain in plain English using a commonly understood vocabulary. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, the first one to be wildly popular. See the price graph in my last essay.
It’s Not Your Daddy’s Bank by William Lama, Ph.D. — Palos Verdes Pulse
Crypto- stands for cryptography which is a means to protect assets including money. In the case of Bitcoin, the money is in digital form, as is the cryptography. A simple example may help. Say I wanted to send a protected message. I could use the “Lama cypher” which says that every third letter after an L is part of the message. So here is a simple crypto-message:
#4LaYI2zLxclH33nLm@o7P&bL7kv8$LZqeCsytLcbP24xmLa5V
I love PV. Got it?
The crypto used in the Bitcoin system is much more complicated.
To understand how it works one needs to know that the Bitcoin system is a collection (network) of computers (also referred to as "nodes") that all run the same Bitcoin software (Bitcoin Core). The original implementation of Bitcoin was created by “someone” called Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. He served as the original maintainer of Bitcoin Core until he disappeared in 2010. Satoshi never identified himself. He is an enigma wrapped in a mystery.
The Bitcoin system is democratic, open to anyone who wants to join the network and play by the rules (protocols). Every node in the system stores an up-to-date list (ledger) of all transactions involving Bitcoin currency since its inception. That way the transactions are transparent, known to all of the roughly 20,000 nodes in the Bitcoin system. We will see that it’s nearly impossible to cheat this system.
How Bitcoin Works
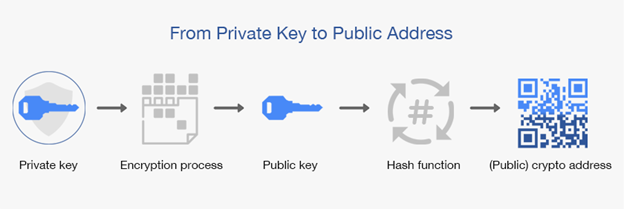
To do a Bitcoin transaction one needs an address and a signature. It all starts with your private key which is a randomly chosen 77 digit number. Then your public key is obtained by running your private key through an algorithm called the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) using readily available software. Your public key is analogous to your bank account number and the private key to your password. Your Bitcoin address is obtained from your public key using more cryptography.
Public Key vs. Private Key (Crypto): Key Differences? | BitIRA®
The first encryption process ECDSA generates the public key and the Hash function produces the address. The hash function takes a digital input of any size and transforms it into a fixed length string of numbers and letters that appear random. The resulting crypto address is the fingerprint of the public key. Bitcoin systems use the Secure Hash Algorithm, SHA256. In this case the crypto address text string has been converted into a QR code to be read by an optical scanner.
Your digital signature is unique for each transaction. It includes your private key and the data inside your transaction message.
For example, say I want to send some Bitcoin to Linda, my spouse. (Aren’t we the cryptopunks?) My message: Send 1/1000 BTC from my bitcoin address to Linda’s bitcoin address. How would the transaction proceed? First, the message is hashed using SHA256 and then that hash and my private key are cryptographically joined to create my digital signature. Since that includes the message, the signature changes with each transaction. At Linda’s end she verifies the transaction and my digital signature using my public key which is published online. Moreover, the 20,000 nodes on the Bitcoin network can also verify the transaction. My message is broadcast to participating nodes who check that my address is linked to a transaction receiving the specific 0.001 BTC that I am sending Linda, that my signature is valid and that her address is accurate. Everything is transparent. How that works is a bit complicated. I’ll explain in the next essay. Stay tuned.
So, what about those Bitcoin wallets that don’t store Bitcoins? The primary purpose of a Bitcoin wallet is to store private and public keys. All Bitcoins are stored in transaction records on the Blockchain. The wallet is also used to create new keys and addresses, construct transactions and sign them with your digital signature, and show how many bitcoins you own in all your addresses. Bitcoin wallets are private, and quite handy gizmos. And what about those miners who don’t search for Bitcoins on the web? To untangle that puzzle we will have to dig into the Blockchain. Look for that in the next installment.
I’ll conclude with another Cryptocurrency silliness. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are “unique and non-interchangeable units of data stored on a digital ledger… that use blockchain technology to establish a verified and public proof of ownership.” Non-fungible token - Wikipedia
NFTs include meme coins, the best known being the cryptocurrency Dogecoin.
And if Bitcoin and Dogecoin don’t strike your fancy, know that there are so many more options, including Doge’s little buddy Shiba Inu at 0.006 cents/coin. SHIBA INU Price Chart (SHIB) | Coinbase There are about 13,000 crypto-currencies on the market, and thousands more are coming, including the Worldcoin. Its founder, Sam Altman, wants to give every single person on the planet some of it for free.
Dr. William Lama has a PhD in physics from the University of Rochester. Taught physics in college and worked at Xerox as a principle scientist and engineering manager. Upon retiring, joined the PVIC docents; served on the board of the RPV Council of Home Owners Associations; served as a PV Library trustee for eight years; served on the PV school district Measure M oversight committee; was president of the Malaga Cove Homeowner's Association. Writes about science, technology and politics, mostly for his friends.
email: wlama2605@gmail.com
Related Articles